Economics – July 2023
Bidenomics is proving effective, as evidenced by a positive and supportive article highlighting the driving force of investments in infrastructure, chip technology, and green initiatives. However, some people question the basis for crediting these recently approved plans for the success. Additionally, they wonder if the 2.4% growth in one quarter truly provides a comprehensive picture. It's possible that we are merely returning to the pre-COVID normal state.
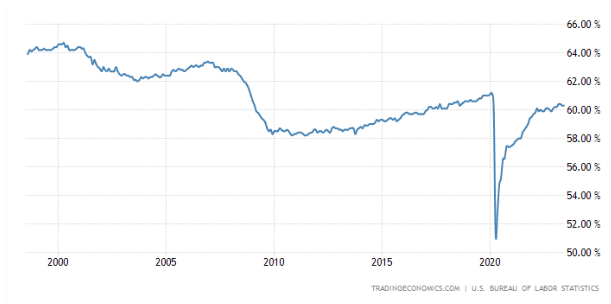
Or are the fifteen million jobs created merely hypothetical?
An infrastructure program
would create 3.4 million jobs in the Southeast, 3.2 million jobs in the Pacific Coastal region, 2.8 million jobs in the Midwest, 2.4 million jobs in the Mid-Atlantic, 1.9 million jobs in the Southwest, and 713,000 jobs in New England. (source)
The PMI index does not reflect the momentum for sustained growth, leading to doubts about its accuracy. Some speculate that the apparent growth may be attributed to increased weapons deliveries, depleting strategic reserves, and the sale of "Russian" gas and oil, which might have been imported via China to Europe. These factors could potentially be influencing the economic situation and need to be considered in assessing the overall economic performance.
US Factory Activity Shrinks the Most in Nearly 3 Years: ISM
The ISM Manufacturing PMI in the United States fell to 46 in June 2023, from 46.9 in May and below forecasts of 47. The reading pointed to a faster rate of contraction in the manufacturing sector since May 2020, with companies managing outputs down as softness continues and optimism about the second half of 2023 weakening. “Demand remains weak, production is slowing due to lack of work, and suppliers have capacity. There are signs of more employment reduction actions in the near term", Timothy Fiore, Chair of the ISM said. In June, declines were seen in new orders (45.6 vs 42.6), production (46.7 vs 51.1), employment (48.1 vs 51.4), inventories (44 vs 45.8) and backlog of orders (38.7 vs 37.5). Also, price pressures eased (41.8 vs 44.2) and the supplier deliveries index increased to 45.7 from 43.5, a sign manufacturing lead times improved again. On the other hand, the customers’ inventories index dropped into ‘too low’ territory (46.2 vs 51.4), a positive for future production. 2023-07-03
Germany on the other Hand is a bit different and
its growth perspective has improved.. Well if if you include statistical errors.
And what about the Sanctions and its influence on the Russian Economy? Information provided
here from the Vienna Institute for International Economic Studies.
After a sharp downturn in Q2 2022, the economy stabilized in the second half of the year and is projected to broadly stagnate in 2023. The overall picture masks the very uneven impact of the war and the sanctions across sectors: while domestic trade and industries that depend heavily on cross-border linkages have suffered, military production and certain import-substituting sectors have flourished. The recently imposed energy sanctions have dealt government revenue a heavy blow and will contribute to budget deficits being much higher in the years ahead.
The recession in Germany and inflation are weighing on the economies of the region, especially in the Visegrád countries. Russia will grow due to an arms boom, Ukraine should recover somewhat.
The Russian Economy in a Graph?
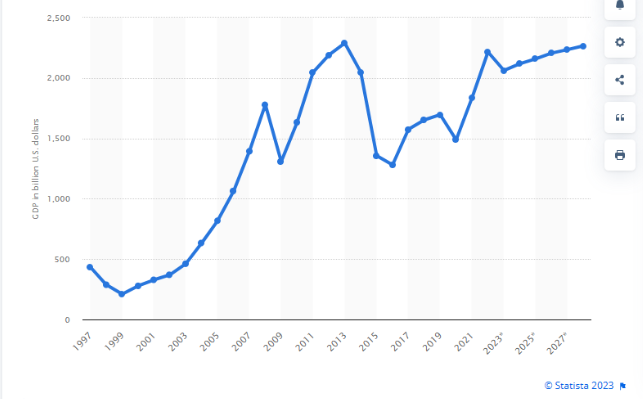
A good year and a half after the start of the Ukraine war, Western sanctions against Russia have missed their target, according to a leading economist. "The sanctions have failed," said Vasily Astrov of the Vienna Institute for International Economic Studies. Despite Western punitive measures and the burdens of the war, Russia is experiencing remarkable economic growth.
"The state and companies have adapted to the war of aggression against Ukraine and Western sanctions at an impressive pace," he said in an interview with the German news channel NTV. Even wages and salaries would rise.
The population will be affected to varying degrees by the sanctions. While the middle class is feeling the sanctions, poorer classes are experiencing positive effects due to labor shortages and higher wages. In general, private consumption has recovered quickly after a brief slump at the beginning of the war.
Overall, the sanctions have largely failed, Astrov concludes. Only the European import embargo on oil and the restrictions in the high-tech sector could have a long-term impact on Russia. Nevertheless, this is not enough to force President Putin to give in, according to experts.
Read the original German text here.
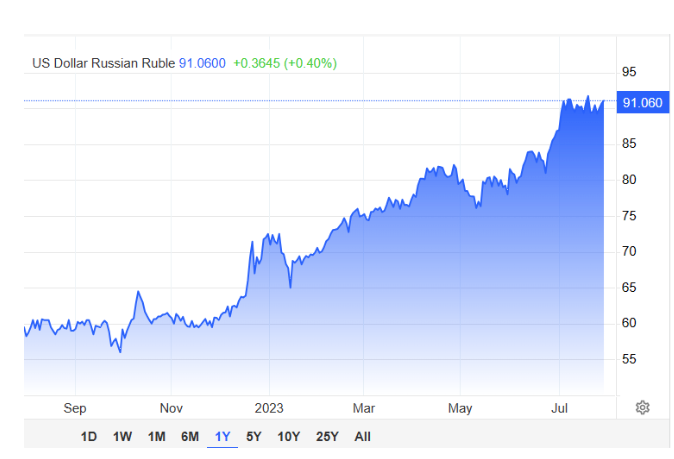
Finally, here is an opinion piece on Russia from people that claim
Bidenomics work.. You may notice
some good differences. As for the Ruble, not sure why they claim it lost all its value?
Graph Source



Sign Up For Our Newsletter
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Please try again later






